What is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) you may ask? It is the wireless non-contact use of radio frequency waves to transfer data. Tagging items with RFID tags allows users to automatically and uniquely identify and track inventory and assets. RFID takes auto-ID technology to the next level by allowing tags to be read without line of sight and, depending on the type of RFID, having a read range between a few centimeters to over 20+ meters.
How RFID works.
RFID has come a long way from its first application of identifying airplanes as friend or foe in World War II. Not only does the technology continue to improve year over year, but the cost of implementing and using an RFID system continues to decrease, making RFID more cost-effective and efficient.
Types of RFID
Within the Electromagnetic Spectrum, there are three primary frequency ranges used for RFID transmissions – Low Frequency, High Frequency, and Ultra-High Frequency.
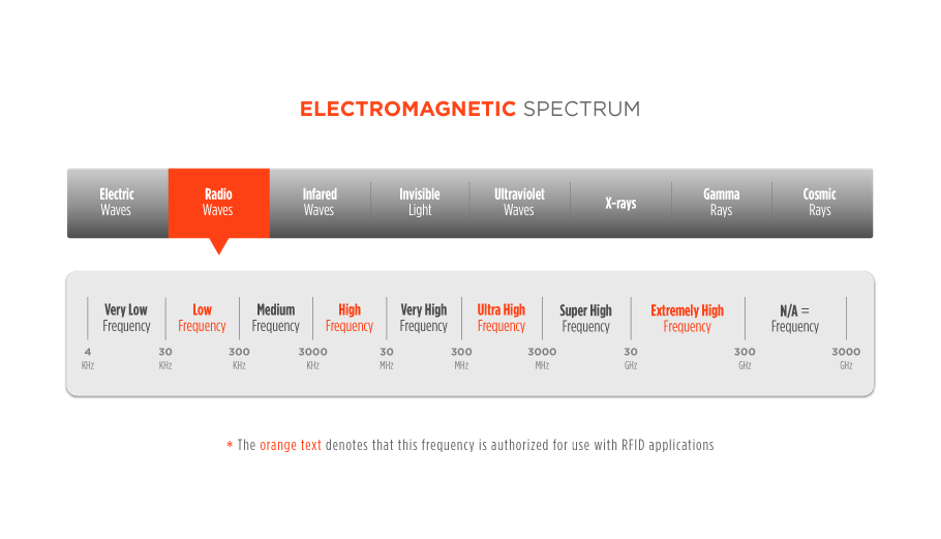
Low Frequency
- General Frequency Range: 30 – 300 kHz
- Primary Frequency Range: 125 – 134 kHz
- Read Range: Contact – 10 Centimeters
- Average Cost Per Tag: $0.75 – $5.00
- Applications: Animal Tracking, Access Control, Car Key-Fob, Applications with High Volumes of Liquids and Metals
- Pros: Works well near Liquids & Metals, Global Standards
- Cons: Very Short Read Range, Limited Quantity of Memory, Low Data Transmission Rate, High Production Cost

High Frequency
- Primary Frequency Range: 13.56 MHz
- Read Range: Near Contact – 30 Centimeters
- Average Cost Per Tag: $0.20 – $10.00
- Applications: DVD Kiosks, Library Books, Personal ID Cards, Poker/Gaming Chips, NFC Applications
- Pros: NFC Global Protocols, Larger Memory Options, Global Standards
- Cons: Short Read Range, Low Data Transmission Rate

Ultra-High Frequency
- General Frequency Range: 300 – 3000 MHz
- Primary Frequency Ranges: 433 MHz, 860 – 960 MHz

There are two types of RFID that reside within the Ultra High Frequency range: Active RFID and Passive RFID.
Active RFID
- Primary Frequency Range: 433 MHz, (Can use 2.45 GHz – under the Extremely High Frequency Range)
- Read Range: 30 – 100+ Meters
- Average Cost Per Tag: $25.00 – $50.00
- Applications: Vehicle Tracking, Auto Manufacturing, Mining, Construction, Asset Tracking
- Pros: Very Long Read Range, Lower Infrastructure Cost (vs. Passive RFID), Large Memory Capacity, High Data Transmission Rates
- Cons: High Per Tag Cost, Shipping Restrictions (due to batteries), Complex Software may be Required, High Interference from Metal and Liquids; Few Global Standards
Passive RFID
- Primary Frequency Ranges: 860 – 960 MHz
- Read Range: Near Contact – 25 Meters
- Average Cost Per Tag: $0.09 – $20.00
- Applications: Supply Chain Tracking, Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Electronic Tolling, Inventory Tracking, Race Timing, Asset Tracking
- Pros: Long Read Range, Low Cost Per Tag, Wide Variety of Tag Sizes and Shapes, Global Standards, High Data Transmission Rates
- Cons: High Equipment Costs, Moderate Memory Capacity, High Interference from Metal and Liquids

